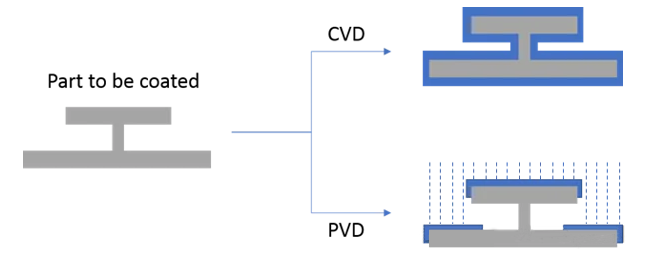
Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) is an important thin film deposition technology, often used to prepare various functional films and thin-layer materials, and is widely used in semiconductor manufacturing and other fields.
1. Working principle of CVD
In the CVD process, a gas precursor (one or more gaseous precursor compounds) is brought into contact with the substrate surface and heated to a certain temperature to cause a chemical reaction and deposit on the substrate surface to form the desired film or coating. layer. The product of this chemical reaction is a solid, usually a compound of the desired material. If we want to stick silicon to a surface, we can use trichlorosilane (SiHCl3) as the precursor gas: SiHCl3 → Si + Cl2 + HCl Silicon will bind to any exposed surface (both internal and external), while chlorine and hydrochloric acid gases will be discharged from the chamber.
2. CVD classification
Thermal CVD: By heating the precursor gas to decompose and deposit it on the substrate surface. Plasma Enhanced CVD (PECVD): Plasma is added to thermal CVD to enhance the reaction rate and control the deposition process. Metal Organic CVD (MOCVD): Using metal organic compounds as precursor gases, thin films of metals and semiconductors can be prepared, and are often used in the manufacture of devices such as LEDs.
3. Application
(1) Semiconductor manufacturing
Silicide film: used to prepare insulating layers, substrates, isolation layers, etc. Nitride film: used to prepare silicon nitride, aluminum nitride, etc., used in LEDs, power devices, etc. Metal film: used to prepare conductive layers, metallized layers, etc.
(2) Display technology
ITO film: Transparent conductive oxide film, commonly used in flat panel displays and touch screens. Copper film: used to prepare packaging layers, conductive lines, etc., to improve the performance of display devices.
(3) Other fields
Optical coatings: including anti-reflective coatings, optical filters, etc. Anti-corrosion coating: used in automotive parts, aerospace devices, etc.
4. Characteristics of CVD process
Use high temperature environment to promote reaction speed. Usually performed in a vacuum environment. Contaminants on the surface of the part must be removed before painting. The process may have limitations on the substrates that can be coated, i.e. temperature limitations or reactivity limitations. The CVD coating will cover all areas of the part, including threads, blind holes and internal surfaces. May limit the ability to mask specific target areas. Film thickness is limited by process and material conditions. Superior adhesion.
5. Advantages of CVD technology
Uniformity: Able to achieve uniform deposition over large area substrates.
Controllability: The deposition rate and film properties can be adjusted by controlling the flow rate and temperature of the precursor gas.
Versatility: Suitable for deposition of a variety of materials, such as metals, semiconductors, oxides, etc.
Post time: May-06-2024